Given credit card data and account information is now dirt-cheap to buy on the dark web; it no longer makes much sense for criminals to exclusively target financial information – especially since the data must also be sold after it’s stolen. Much more lucrative – and quicker to obtain, are the bitcoins deposited by ransomware victims into a thief’s account.
Welcome to the hottest cyber-criminal activity of today – ransomware. Although ransomware such as PGPCoder has been around for a decade, this exploit only gained wide traction during the past several years. Combining the best of social engineering, e.g., well-crafted spear phishing using publicly available information, including emails of licensed professionals, with botnets usually tasked with promulgating spam, criminals have been able to re-purpose the latest Trojans for a much more lucrative job.
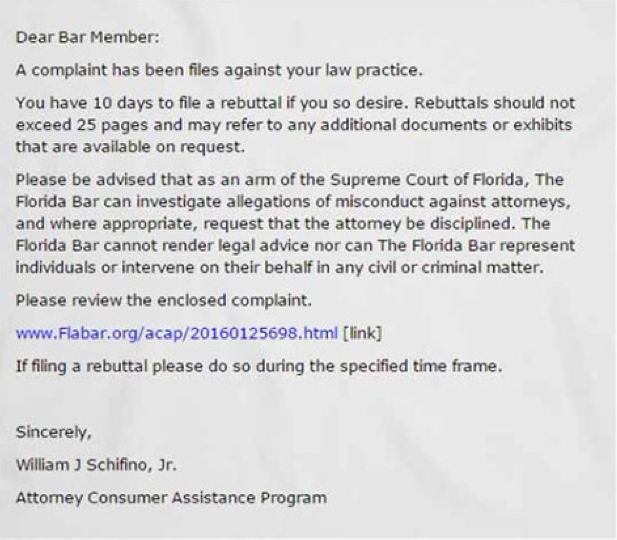
The most recent crop of ransomware scams have successfully targeted professionals. The Florida Bar recently warned its members these phishing exploits can use various subject lines, including “Florida Bar Complaint – Attorney Consumer Assistance Program”. A scam email with “Lawyers and judges may now communicate through the portal” in the subject line uses information found in a June 1, 2016 Florida bar article. Preying on many lawyers’ natural tendency to help, the email asks recipients to “test the portal and give feedback.”
During the past several weeks, Florida lawyers clicking on the masked link found in the above email notice were surprised to learn their entire computer network was held for ransom – automatically encrypted in one fell swoop by criminals half way across the world. Users only become aware of this exploit when they can no longer access their data and see a message on their screen demanding a ransom payment in exchange for a decryption key. The message also includes instructions on how to pay the ransom, usually with a widely traded anonymous digital currency such as Bitcoin or anonymous pre-paid cash vouchers such as MoneyPak and Ukash.
In the same way the IRS would never cold call you about an audit, no bar association would ever deliver a complaint simply by email. Nevertheless, these scams succeed with a good number of professionals who are pressed for time, have computers systems that do not automatically filter executable content or simply just don’t have adequate training. Indeed, even if there is adequate training and sophisticated IT personnel running a firm’s network, law firms are never immune to hacking incidents. This past March, it was reported by The Wall Street Journal that two blue chip firms, Cravath Swaine & Moore LLP and Weil Gotshal & Manges LLP, were among a number of law firm hacking victims. Law firms will always be vulnerable to a direct attack by a sophisticated hacker. A panel of law enforcement specialists in 2015 put it best when they said law firms are seen as “soft, ripe targets for hackers.”
As reported by the Wisconsin Bar Association, the ABA’s Division for Bar Services has been monitoring a rise in ransomware exploits, with recent confirmations of scam emails also sent to lawyers in Alabama, Georgia, and California. The ABA has been working with the FBI to get the word out regarding ransomware – leading to state bars pushing out the message via newsletters and blog posts. In fact, the ABA has been warning lawyers for years regarding data security. Indeed, there is an argument that improved data security helps with the marketing of a law firm.
Although recent attacks have fed on a lawyer’s publicly accessible email address, these very same attacks also go after other professionals. For example, targets include hospitals – where patient information can ill afford to stay locked for a very long time. As well, a growing number of accounting firms are falling prey to ransomware. Ransomware is especially damaging to accounting firms given accountants hold critical financial data of clients that is often deadline-focused. Indeed, there may be significant penalties accessed against clients for untimely filings.
The threats have become more pronounced as criminals realize the benefit of redirecting resources to ransomware aimed at professionals such as lawyers and accountants. A consultant who assists accounting firms guard against ransomware attacks warned accountants last year of the polymorphic Virlock that spawns unique versions after every use so antivirus programs cannot recognize it as well as TeslaCrypt that uses file names associated with well-known online games found on a child’s computer – which can spread to other computers attached to a home network, including an office PC.
As set forth in a 2014 CERT notice, destructive and lucrative ransomware variants include: Xorist, CryptorBit, CryptoLocker, CryptoDefense, and Cryptowall. All of these exploits encrypt files on the local computer, shared network files, and removable media. Although the private decryption keys for CryptoLocker, Xorist, CryptoDefense have since become available – rendering these exploits defensible, recent ransomware variants with no available decryption keys continue to launch. For example, in June 2015, the ABA warned about the CryptoWall ransomware exploit. And, a March 9, 2016 blog post from the security firm TrustWave details a major botnet operator moving from spam campaigns to delivering a new ransomware exploit deploying malicious javascript – the Locky ransomware. Kaspersky Labs also wrote about the Locky ransomware – and its successful targeting of several hospitals. If it has not already done so, it is only a matter of time before the Locky ransomware migrates to lawyers and accountants.
The FBI has addressed ransomware exploits for some time now – likely given it was inadvertently a participant in one such exploit. In 2012, the FBI was spoofed in a Reveton ransomware attack activated when a user visited a compromised website. Once infected, the victim’s computer immediately locks, and the monitor displays a screen stating there has been a violation of federal law. The bogus message goes on to say that the user’s Internet address was identified by the FBI as having been associated with child pornography sites or other illegal online activity. To unlock their machines, users are required to pay a fine using the MoneyPak prepaid money card service.
According to an April 29, 2016 FBI Bulletin, the FBI saw a pronounced increase in ransomware attacks in 2015 – with a projection that it will grow a great deal more during 2016. Despite the fact it will always be easy to pay ransom given the instructions are explicit and the amount sought can be in the $400 range, the FBI doesn’t support paying a ransom in response to a ransomware attack: “Paying a ransom doesn’t guarantee an organization that it will get its data back [and] not only emboldens current cyber criminals to target more organizations, it also offers an incentive for other criminals to get involved in this type of illegal activity. And finally, by paying a ransom, an organization might inadvertently be funding other illicit activity associated with criminals.”
Instead, the FBI suggests the key areas to focus on with ransomware are prevention, business continuity, and remediation. Given that ransomware techniques are rapidly evolving, business recovery and continuity become even more crucial. More to the point, as recognized by the FBI: “There’s no one method or tool that will completely protect you or your organization from a ransomware attack.” Instead, the FBI suggests firms focus on a variety of prevention efforts – in terms of awareness training for employees and technical prevention controls, as well as the creation of a solid business continuity plan in the event of a ransomware attack. Planning for disaster can never be considered wasted time. And, after a ransomware attack is suspected, victims should immediately contact the local FBI field office and report the incident to the Bureau’s Internet Crime Complaint Center.
If a firm has a proactive approach, there are certainly some basic things that can be done today to avoid a ransomware exploit. In an effort to help its constituency, the ABA has conveyed some basic technical defenses against ransomware:
- Block executable files (such as “.exe” files) and compressed archives (such as zip files) containing executable files before they reach a user’s inbox.
- Keep operating systems, browsers and browser plug-ins, such as Java and Silverlight, fully updated.
- Program hard drives on your computer network to prevent any unidentified user from modifying files.
- Regularly back up data with media not connected to the Internet.
As for the most basic of “basic training”, law firm administrators are being awakened to this threat with some sound advice that never gets old: “Be smart. Be aware. Don’t open or click on anything that looks suspicious. They won’t come in if you don’t open the door.” In other words, never click on a link, file or image from an untested source or untrusted URL. The extra seconds it takes to confirm the actual sender of an email message or owner of a website is well worth the time.
Given that business continuity best practices should mesh with IT security best practices, backups should obviously be stored outside the network. And, if you are forced to restore from a backup it is never wise to restore your data over existing production data. Consulting with a disaster recovery specialist before disaster strikes probably is a good idea.
Professionals – especially lawyers and accountants should also consider purchasing insurance that covers ransomware losses – including the related IT expenses. Such insurance is typically purchased using a standalone policy that has been around for years. There are some malpractice insurers, however, e.g., CPAGold, who provide such coverage directly in the policy. Tech vendors and legal counsel associated with these carriers typically have years of experience handling these incidents and can be rapidly deployed to address any situation.
Given the serious threat of ransomware, businesses large and small are reminded to at least do the basics – train staff regarding email and social media policies, implement minimum IT security protocols, regularly backup data, plan for disaster, and regularly test your plans.